Genetics and strains
Understanding cannabis strains origin
to make an informed choice
What is cannabis genetics ?
The genetics of a cannabis plant define its identity, from its category (indica, sativa, hybrid, ruderalis) to its cannabinoid profile, size, and shape. But how is a strain's genetics determined?
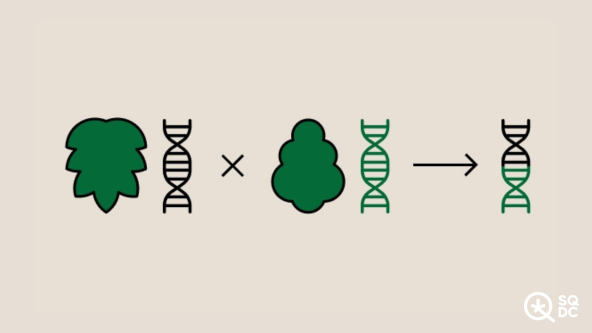
In the field of cannabis, genetics refer to the transfer of genes from two "parent" strains to their "offspring", thus creating a new strain. In other words, the genetics of a cannabis product correspond to the two "parent" strains that have been crossed.
Cannabis is a dioecious plant, meaning it develops either male or female reproductive organs. It is the female plants that produce the flowers and trichomes that we consume. The flowers of female plants have small hairs called pistils, which capture pollen released by the floral clusters of male plants.
Once fertilized, a female cannabis plant will produce seeds that can exhibit various genetic variations inherited from both parents. The genetics of a cannabis plant can be manipulated by selecting specific male and female strains to develop unique characteristics such as:
- Plant convenience
- Disease resistance
- Yield
- Stability of cannabinoid levels
- Etc.
- Flower attributes
- Variety and category
- Color
- Odor
- Cannabinoid levels
- Terpene profile
- Size and shape
- Effects*
- Etc.
Certain cannabis genetics may produce distinct effects depending on their classification. While the "indica" category may induce a relaxing effect, the "sativa" category may induce a stimulating effect. These effects can vary from person to person based on numerous factors. Learn more about the effects of cannabis.
Video available in French only
The rule for writing the genetics of a product is widely accepted in the cannabis field, and even in biology in general: the female plant strain should always be listed first.
Example :
(F)Lemon Skunk x (M)Amnesia Haze
What is an landrace cannabis strain?
Also called "traditional", "ancestral", or " indigenous ", landrace strains refer to a small number of cannabis varieties that evolved naturally in the geographical regions where they were discovered and were not created or manipulated by humans. They thus retain the genetics and characteristics specific to their environment.
Today, due to massive hybridization, it is highly unlikely to find a purely indica or purely sativa cannabis plant. Over time, species have been blended to obtain specific characteristics (e.g., increasing cannabinoid potency, achieving particular aromatic profiles, etc.), giving rise to hybrid strains, which are now predominantly found on the market.
Video available in French only
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
For those who want to go further, let's explore the difference between genotype and phenotype.
Genotype
The genotype represents the range of genetic possibilities of a variety obtained from its parents. In other words, it is the genetic makeup of the plant.
The genotype is expressed within the DNA.
Phenotype
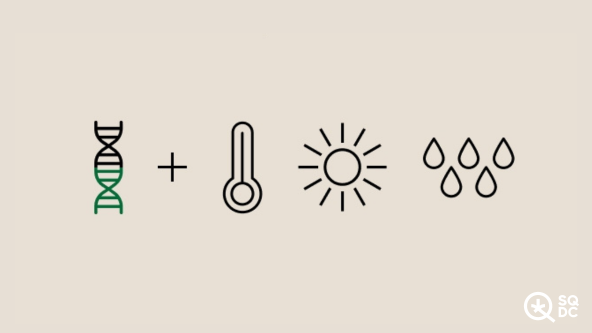
The phenotype represents the physical expression of the genetic makeup (genotype), which can be influenced by several factors.
The phenotype is expressed through characteristics such as color, size, height, smell, cannabinoid levels, terpene profile, plant yield, disease resistance, and more.
Female and male plants each transmit a genetic makeup during pollination, and this genetic makeup (genotype) will express itself in different ways (phenotype) as the seed grows into a plant.
That said, not all seeds from the same pollination will express themselves in the same way. Since the genotype of the seed interacts with its growing environment, factors like temperature, light access, humidity levels, soil type, and even wind strength will influence the phenotype, or the physical expression of the plant.
Video available in French only
In summary, color, size, smell, cannabinoid levels, terpene profile, yield, disease resistance, and other attributes can differ from one seed to another, even if they come from a pollination of identical parents. This helps explain why the same genetic cross can appear in two different products or why the same variety can be found in two different categories.
Choose the right product
It is important to choose a cannabis product and consumption method based on your level of experience, state of health and tolerance for potentially unpleasant effects. For personalized advice, speak with an in-store advisor or see the "Types of Products" section.

Want to speak to an SQDC advisor?
Our advisors are online!
Click on the SQDC icon in the bottom right-hand corner of any page to start a conversation with one of our in-store advisors!

Frequently asked questions
Products
-
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
The genotype is the set of genes that a plant inherits from its parents. The phenotype is the way these genes physically manifest, influenced by internal and external factors.
-
What is a landrace strain?
Landrace strains , also called "traditional" , "ancestral", or "indigenous", are types of cannabis that have evolved naturally in their region of origin without human intervention. They therefore retain their natural characteristics. Today, it is rare to find a cannabis plant that is purely indica or sativa.
-
Why do we find a genetic cross with an "unknown" variety?
It may happen that one of the varieties used for the genetic cross is simply not known to the supplier.
-
If all strains are technically hybrids, why do we continue to categorize them as "indica" and "sativa"?
The choice to classify a product into one of the three categories (indica, sativa, or hybrid) is based on its biological predominance (physical characteristics, genotype, etc.) and its potential effects. If a product is classified as indica, it means its dominant characteristics belong to that category. The same goes for products in the sativa category. If a product is classified as hybrid, it possesses characteristics of both other categories in an equivalent way.
-
How will the genetics of a "rotating" product or one from a "blend" be listed?
The genetics of these types of products will not be listed .
-
Where does the information about the genetics of SQDC products come from?
Like other information related to a product's attributes, the genetic cross information of each product is voluntarily provided directly by the supplier, who ensures its accuracy.
-
Why does this strain at SQDC appear in both the "indica" and "sativa" categories?
A cannabis plant adapts to its growing environment. Although it comes from the same genetics, a plant may display different characteristics and therefore be categorized differently.
Additionally, the order of the strains used (female or male) could affect the transmitted genetics according to certain studies.
-
Why does a product with the same genetic cross not have the same product name?
Besides the concept of phenotype, the supplier may simply decide to name a variety differently (e.g., La Cerise sur le Funday = Sage and Sour ).
-
Why do we find similar names in genetics like Chem D, Chem Dawg, Chemdawg, Chemdog, etc.?
These are indeed the same genetics, but the spelling can vary by region and supplier.
Other articles you might like

Why do product’s THC and CBD levels vary from batch to batch?
The cannabinoid concentration of the same cannabis product can vary from batch to batch. Find out why in this article.

The Little Cannabis Glossary
Consult our cannabis lexicon to learn more about the terms and vocabulary commonly used to talk about cannabis.

What are cannabinoids?
Explore the major cannabinoids (THC and CBD), their effects on the body, tips for choosing products and more.
Références :
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3736954/
- https://cannabismuseum-amsterdam.com/landrace-strains/
- https://earthmed.com/blog/8-of-the-most-popular-landrace-strains#:~:text=Landrace%20strains%20refer%20to%20those,high%20desirability%20for%20recreational%20benefits.
- https://acreagepharms.ca/landrace-strains/
- https://herb.co/news/culture/what-was-the-original-strain-of-weed/
- https://www.zamnesia.com/blog-landrace-5-oldest-cannabis-strains-n216
- https://dutch-passion.com/en/blog/what-are-cannabis-landrace-strains-n1006
- https://honestmarijuana.com/landrace-strains/
- https://www.royalqueenseeds.com/blog-landrace-cannabis-in-search-of-the-missing-genotype-n461
- https://cannigma.com/plant/cannabis-landrace-strains/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tBGtvVJLPiY
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JECOyyMqyYg
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/indica-vs-sativa#hybrids
