The major cannabinoids:
The difference between CBD and THC
Learn about THC and CBD – how they work, their chemical makeup
and the potential effects – along with tips for choosing between products.
THC and CBD: introduction
The two cannabinoids most present in cannabis in its natural state are THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol).
When consumed, THC and CBD both affect the body and the mind, but they do so in different ways.
- CBD usually doesn’t have an intoxicating effect. In other words, it doesn’t create the kind of euphoric feeling or “high” more typical of THC.
- CBD increases or improves the body’s own production of cannabinoids (small molecules produced by our bodies that help regulate our mood, sleep and even appetite). THC, on the other hand, temporarily replaces the body’s cannabinoids, binding to receptors in the body in their place.
- Some studies show that when CBD and THC are taken together, the CBD may moderate some of the THC’s psychoactive effects. However, more research is required.1.
Understanding how CBD and THC work can help you choose the products best suited to you.
How do THC and CBD affect the human body?
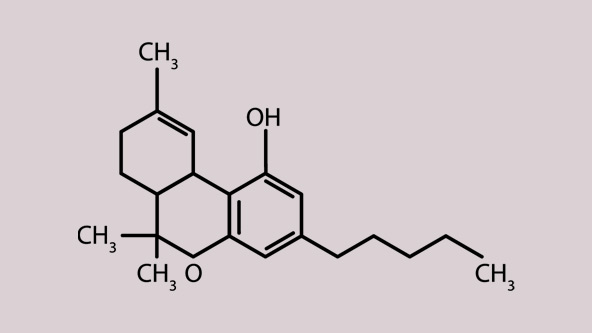
How THC works
THC, whose scientific name is delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, is a naturally occurring chemical compound (cannabinoid) in cannabis plants. It’s the main compound responsible for cannabis’ psychoactive and intoxicating effects.
THC acts on our endocannabinoid system
THC interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which is responsible for several aspects of our health and well-being (weight control, body temperature, heart rate, etc.).
The system has two main components:
- endocannabinoids, molecules naturally produced by the body, and
- cannabinoid receptors, located in our central nervous system, brain, etc.
Endocannabinoids function a little like keys that fit into the receptors and unlock the transmission of messages between cells. Because it’s a cannabinoid, THC also fits into the receptors, temporarily replacing the body’s natural endocannabinoids and triggering a range of effects.

The higher a product’s THC content, the bigger the risk that the effects will be strong.
Potential effects
Products containing THC are responsible for most of the short and long-term psychoactive and physical effects sought by users, such as relaxation or even euphoria, the later usually described as being “stoned,” “high,” “baked” or “buzzed.”

The effects of a given product can vary from person to person based on a number of factors, including age, gender, weight, medical history, etc.
Potential risks
THC poses certain health risks and can sometimes have undesirable short and long-term side effects on the body and mind.
Here’s a simple overview of the potential risks involved when using cannabis-based products that contain THC:
Various effects:
- THC can affect the body and mind in various and sometimes unpredictable ways.
Overdosing:
- Though rarely fatal, overdoses can often require medical treatment due to the occasionally intense and alarming effects.
Risks from regular use:
- Repeated use may affect memory and concentration and, in some cases, lead to more serious issues, such as breathing problems, cardiovascular disease and cannabis use disorder.
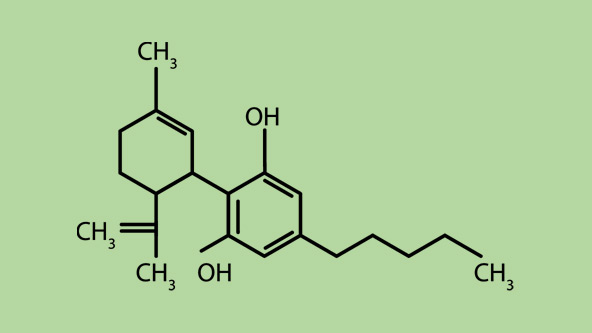
How CBD works
Cannabidiol, commonly referred to as CBD, is a cannabinoid that occurs naturally in hemp and cannabis flowers. Unlike some other compounds, CBD alone does not trigger any intoxicating or euphoric effects. That said, while it may be considered unintoxicating, this compound could still influence the user’s experience. Our scientific understanding of CBD remains limited and does not allow us to accurately say what this influence is or how it works.
CBD acts on our endocannabinoid system
Like THC, CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system. However, it does so in different ways.
As a reminder, the endocannabinoid system has two main components:
- endocannabinoids, molecules naturally produced by the body, and
- cannabinoid receptors, located in our central nervous system, brain, etc.
Endocannabinoids connect to the body’s cannabinoid receptors, facilitating communication between cells. Research suggests that CBD inhibits an enzyme responsible for regulating and eliminating excess endocannabinoids and stimulates the development of cannabinoid receptors, making the endocannabinoid system more receptive and efficient. However, research into CBD remains limited and it is currently impossible to say with any certainty what CBD’s effects on the user experience are.
Potential effects
In high doses, CBD may, for example, favour relaxation, instill a feeling of calm or cause drowsiness for some people. It may also temper some of THC’s unpleasant effects, such as paranoia or anxiety. However, these claims cannot be proved with any certainty1. Ongoing research into the compound aims to gain a clearer understanding of its properties.

The effects of a given product can vary from person to person based on a number of factors, including age, gender, weight, medical history, etc.
Potential risks
Even if CBD has few if any euphoric properties or intoxicating effects, it remains a psychoactive cannabinoid that can affect users’ psychological and cognitive functions.

The THC and CBD in dried cannabis (flowers, ground and pre-rolled) do not have any noticeable effects unless they are activated by the high temperatures produced by burning, vaporizing, or decarboxylating cannabis.
How to choose a product?
THC intensity
Use these icons to determine the degree of THC intensity in our products

0 - 10 %

> 10 - 20 %

> 20 %
Dominance
Discover the dominance of the THC and CBD cannabinoids in our products with ease thanks to these icons.



The right product for your needs
It’s important to choose a cannabis product and a mode of consumption that suits one’s level of experience, state of health, and tolerance towards certain potentially unpleasant effects. For personalized tips, please do not hesitate to consult our Buying guide.

You would rather speak to an SQDC professional?
Our advisors are online!
Click on the SQDC icon in the bottom right-hand corner of any page to start a conversation with one of our in-store advisors!

Frequently asked questions
Products
-
How long do the effects of CBD and THC last?
The duration of the effects of CBD and THC can vary depending on several factors including the mode of consumption, the administered dose, and the individual. In general, the effects can be felt for as long as 8 hours with oral or sublingual administration methods typically having a longer duration of action than inhalation methods.
-
Why choose CBD?
People consume CBD for a variety of reasons, but these are often linked to its relaxing properties. In fact, CBD possesses little to no euphoric properties. At higher doses, it may cause drowsiness for some people or create a sense of calm. Some studies are exploring its potential to modulate unpleasant THC effects, such as paranoia or anxiety. However, be aware that it is not yet possible to determine with any certainty that CBD presents beneficial effects when consumed. At this point in time, studies have not sufficiently proven these effects.
-
What is the THC and CBD content of the cannabis sold at the SQDC?
THC and CBD content vary from product to product. For specifics about the make-up of the products sold at the SQDC, see the product sheets in the Products section.
-
Does CBD remain in the body?
Yes, CBD can remain in the body for a few days to many weeks after the last use, depending on the frequency and quantity that was consumed, the metabolism of the individual, and the method of use. In general, CBD is estimated to have a half-life of 2 to 5 days for occasional use, but this can vary considerably from one person to the next.
-
Who can’t take CBD?
The consumption of CBD is not generally recommended for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding, or children, due to a lack of research in these areas. In addition, people who have certain medical conditions or take specific medications should consult a healthcare professional before trying CBD in order to avoid any unwanted interactions.
-
Is there THC in CBD?
No, CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) are two distinct cannabinoids derived from the cannabis plant. They differ both in terms of chemical structure and their effects on the human body. Certain CBD-based products, however, can contain traces of THC, depending on the method of extraction and the source plant, but also local regulations.
-
What is the difference between CBD and THC?
The consumption of THC and CBD has a distinct effect on the body. THC is the main psychoactive compound in cannabis. It produces the majority of the psychoactive and physical effects. CBD, on the other hand, possesses little to no euphoric properties.
Other articles you might like

Why does the cannabinoid concentration vary within the same product?
The cannabinoid concentration within the same cannabis product can vary from batch to batch. Discover why in this article.
Practical guide to the new units of measure for THC and CBD concentration
All dried or ground flower products, pre-rolls, oils, and oil sprays now display the concentration of cannabinoids in miligrams per gram (mg/g).

How do I read the tag on a dried or ground cannabis product?
For your convenience, we prepared a list of five important things to look out for.
Sources :
- Health Canada. (2023). Drugs and medication > Cannabis. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/drugs-medication/cannabis/information-medical-practitioners/information-health-care-professionals-cannabis-cannabinoids.html
- Whiting PF, Wolff RF, Deshpande S, Di Nisio M, Duffy S, Hernandez AV, Keurentjes JC, Lang S, Misso K, Ryder S, Schmidlkofer S, Westwood M, Kleijnen J. (2015). Cannabinoids for Medical Use: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA. 313(24), 2456-73.
- Government of Canada. (2023). Cannabis and your health. https://www.canada.ca/en/services/health/campaigns/cannabis/health-effects.html
